QD TV: What is it? Quantum Dot vs. OLED TV
by Jack Burden, Senior Contributor
QD TV is a new television technology that is taking many of its cues from OLED TV (organic light emitting diode) technology. It consists of extremely small light-emitting crystals called quantum dots. These quantum dot TVs may be ( I say maybe because we have learned that nothing is certain in the television industry with new technological developments) available by late 2012 or 2013. But are they just another name for OLED TVs?
Similarities with OLED technology
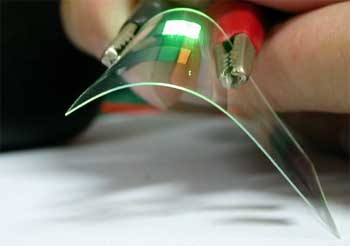 That's a good question. When we read the specifications and technological reports on QD technology they look suspiciously similar to OLED technology. For example, OLED cells do not need a backlight, are extremely thin and are based on liquid crystal cells – all traits that QD technology claims. OK maybe they are not claiming the compounds used are organic, but they must be for all these compounds and phosphors are really natural or organic substances. If we wanted to, we could call plasma TVs, organic plasma TVs due to the organic or natural phosphors used. Another similarity between the two is the claim of a flexible screen in the future. That is a claim that we heard from OLED manufacturers at the beginning as well.
That's a good question. When we read the specifications and technological reports on QD technology they look suspiciously similar to OLED technology. For example, OLED cells do not need a backlight, are extremely thin and are based on liquid crystal cells – all traits that QD technology claims. OK maybe they are not claiming the compounds used are organic, but they must be for all these compounds and phosphors are really natural or organic substances. If we wanted to, we could call plasma TVs, organic plasma TVs due to the organic or natural phosphors used. Another similarity between the two is the claim of a flexible screen in the future. That is a claim that we heard from OLED manufacturers at the beginning as well.
So how thick are the screen depths? We've already seen .25 inch OLED TVs displayed and Sony even produced one for sale – the Sony XEL-1. QD will likely be the same and no better in terms of screen or panel or layer depth capability. Energy usage on both is low due to the high efficiency of the crystals, so large displays are a good possibility for both technologies.
Both OLEDs and quantum dots can also be printed onto substrate, or plastic or other materials or developed into a super thin multi layer nanofilm.
Another similarity is that the cells from both are excited (OLED) or activated (QD) by a very slight electric current. Both are extremely energy efficient in this regard. In the case of OLED TVs – they are charged by the thin film transistor backplane. For QD we dont know what the charge source will be yet but probably the same or similar for televisions. Or it could be from small LED lighting.
Differences with Quantum Dots
So what is the major difference between these two upstart technologies? It looks like whether the color producing crystals are organic or inorganic is the primary difference. As we know, many of the first OLED had blue phosphors that only lasted about 7000 hours and we suspect the red and green phosphors were not much better. Now, those numbers have increased considerably. But OLEDs are made from rare earth materials and thus are expensive to produce as those materials become harder to get. Qds are made from inorganic semiconductor crystal substance which is one of the reason manufacturers are probably excited about the technology. It will likely be much less expensive to produce.
Another difference is is that OLEDs directly emit light whereas Qds conduct pass through light, thus OLEDs would theoretically have slightly better viewing characteristics in this regard from the off angle viewing perspective.
Supposedly, many of the same companies that develop OLED technology are supporting QD. Sony, Samsung, LG and Sharp are rumored to be the main TV manufacturers assisting with the development of the technology.
How does it work?
A simple definition of what a quantum dot is - a semiconductor (crystal matter for our purposes) with three spacial dimensions. Quantum Dot is a term coined by Yale professor and American Physicist Mark Reed.
How does QD technology work? Color is changed in this technology by altering the size and shape of the minuscule crystals produced.





